What is 5G
For the past couple of years, there have been talks of faster mobile internet through 5G technology. Now 5G is being deployed in many areas across the world, and smartphone manufacturers have started releasing phones with 5G. In the next few years or less, we may be able to download full HD movies in mere seconds, as opposed to minutes using 4G LTE. Now you may be thinking, that’s really not much of a difference, I don’t mind waiting a couple of minutes to download a movie.
5G is the next standard for wireless internet connectivity after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G LTE, and obviously will be much much faster than 4G LTE. It is defined as any system using 5G New Radio(5G NR). Initially, 5G rollout is expected to be done with existing 4G infrastructure using 5G NR software(Non-standalone mode), and later the hardware will be upgraded(Standalone mode) as well. In the non-standalone mode, existing 5G network will be used for control functions. Basically, the initial connection will be handled by the 4G network which will then be switched to 5G. While the full capabilities of 5G will not be available in this mode, it will help carriers to switch to 5G without having to deploy 5G hardware all at once. And all 5G devices will be able to use 4G networks as well.
Deployment of 5G began in 2019, and currently, South Korea, China and the United States are leading in 5G deployment. While 4G was mostly restricted to mobile devices, the increased bandwidth, as well as higher speeds(up to gigabits per second) promised by 5G, may result in them being used for connectivity in laptops, PCs and other devices.
Based on the frequency spectrum used, 5G can be Frequency Range 1 (FR1; from 450 MHz to 6GHz) and Frequency Range 2(from 24.25GHz to 52.6 GHz). FR1 has a higher range, and can penetrate buildings more easily, and therefore will require fewer cells. Even though the speed is limited, you can expect most of the companies to initially roll out 5G using FR 1. The higher frequency spectrum, often referred to as the millimetre-wave offers internet at much higher speeds, but it requires more cells as it has very low penetrating power.
The real impact of 5G does not lie in faster download speeds for your smartphone. 5G doesn’t just mean higher bandwidth(higher Mbps), but also lower latency. A higher bandwidth may mean faster download speeds for a movie, but a lower latency means a faster response to over the network inputs. That is going to accelerate any technology that relies on cloud computing. Have a look.
IoT
With the arrival of 5G, the capabilities of IoT systems will increase to a large extent. A larger number of sensors can be deployed and combined with the low latency offered by 5G, the systems will be capable of detecting and responding to smaller changes. A lower latency will also mean that a lot more processing can be done in the cloud, leading to cheaper and less bulky systems without compromising the near real-time implementation of corrective action.
A connected network is only as robust as the connections. For example, a network of sensors and cameras connected together to detect theft, or to prevent spoilage of food while being transported, is only as good as the network that connects them to the servers that can make the necessary changes. When a sensor detects a possible equipment failure, the operators need to be alerted fast enough, and without fail, to avoid further damage. With the improvement in network stability over 5G, IoT systems could be more robust and bring about energy savings, and improved capabilities.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence systems may be getting a leap forward with 5G. With more advanced IoT systems, AI systems get more data. And better data means better models which means better results.
Faster and low latency networks can also solve a common problem faced by AI systems: the enormous computational resources required. Complex AI systems process large amounts of data to get meaningful conclusions and often most of the processing is therefore done on cloud servers, but for some applications, cloud computing is simply not fast enough.
The best example of this would be self-driving cars. These cars are loaded with sensors and cameras which presents a large amount of data every second. For a car to drive itself, an artificial intelligence system needs to process all this data, and output control signals in near real-time. And it needs to do this without a break and without a mistake. Therefore, currently, all self-driving cars have powerful computers in them. And this makes self-driving very expensive.
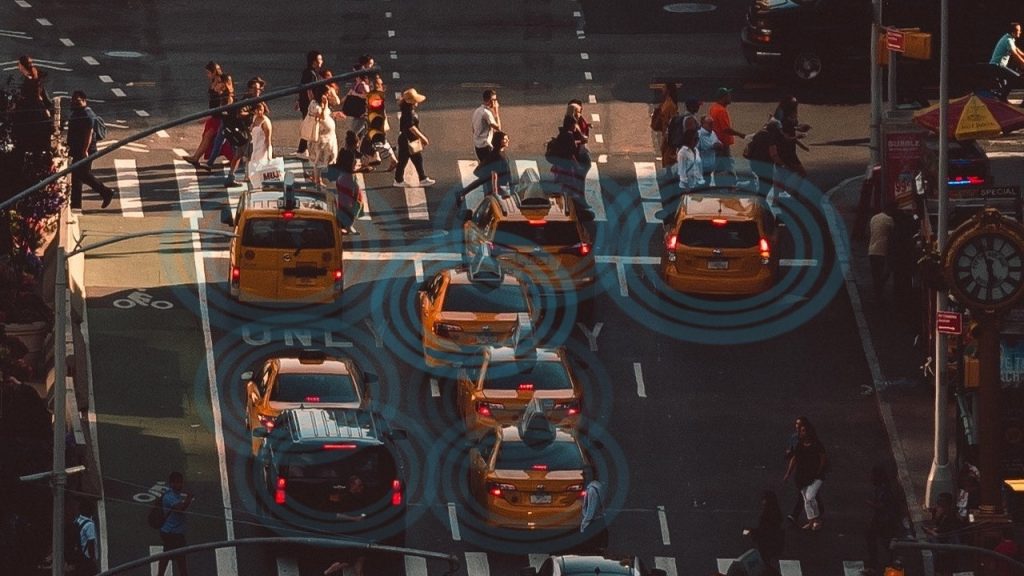

But what if you could send the data to the cloud, process it, and send back the control signals? That will bring down the cost of an individual car to a large degree. With 4G, this was unthinkable. But with the widespread adoption of 5G, this may very well become true. At least some data can be processed in the cloud.
That may not be the only innovation that can happen with 5G and the automobile industry. 5G may bring AI systems capable of analysing and optimising traffic patterns, avoid accidents, and connected cars much closer to reality.
Cloud gaming
The major drawback right now with cloud gaming is the latency. When you’re watching a movie, there’s not a lot of back and forth communication between your device and the servers, but while gaming, the rendered game changes with every input. When you fire, you want to see it happening instantly, even a small delay can ruin the game for you.
As the distance from the server increases, the problem also increases. But with 5G internet, this may change. The low latency offered by 5G can give you a gaming experience equal to that of console gaming. The law hardware investment required for cloud gaming, combined with the low latency of 5G can bring a lot of people to get into cloud gaming.
And, 5G can also make VR cloud gaming closer to reality. VR games usually require pricey hardware, and because of the nature of the content, they’re not easy to stream. While Shadow is starting a VR streaming service for users in the US, they require a fibre optic connection. But as 5G becomes more widespread, we may see a lot of cloud gaming platforms offering VR games.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine has come a long way in the last decade. Now it is possible to consult a doctor while you’re in your bedroom. There are many apps that let you see a doctor over text, or a phone call or a video call. Patients can get their prescriptions without getting out of their house. But, it is still very limited. Even if you need to take a simple body temperature reading, you need to see a doctor. Sure you can do it with a thermometer at home, but if the doctor needs to do some procedures, that’s not possible.
And the telemedicine is not limited to consulting your doctor without leaving your home. In rural areas, the number of doctors is very limited. And even in areas where doctors are available, expert surgeons needed for a specific type of surgery may not be available.
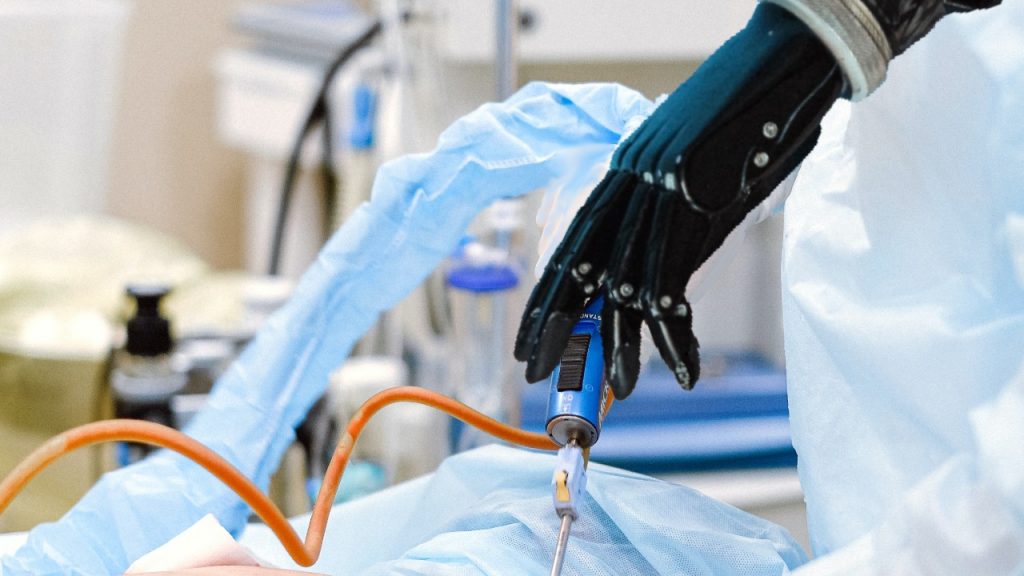
But with 5G, doctors will be able to perform surgeries without even being in the room. In fact last year in China, successful tests were completed on telesurgery. While the tests were highly limited (robots performed preplanned procedures based on commands from doctors situated far away), with 5G and advances in VR, it may not be long before surgeries are done completely remotely.




